publications
publications in reversed chronological order.
2026
-
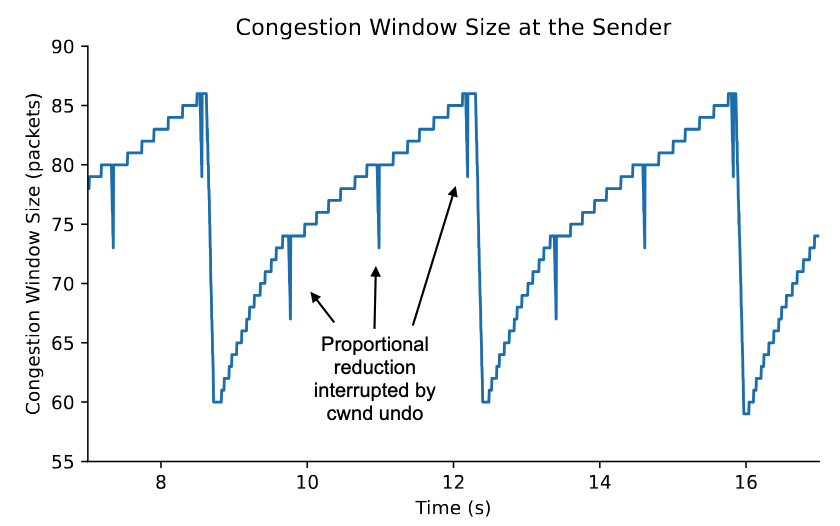 Backbone Switches No Longer Need to Deliver Packets in SequenceUfuk Usubütün, Fraida Fund, and Shivendra PanwarIn review at IEEE OJCOMS, 2026
Backbone Switches No Longer Need to Deliver Packets in SequenceUfuk Usubütün, Fraida Fund, and Shivendra PanwarIn review at IEEE OJCOMS, 2026Building Internet switches becomes harder and costlier as line rates increase. The vulnerability of classical TCP loss detection to packet reordering has traditionally required switch designs to deliver packets in sequence. Consequently, simple and efficient designs, such as the Load Balanced Birkhoff-von Neumann Switch, were considered impractical. With modern TCP implementations employing loss-detection algorithms such as Recent Acknowledgment (RACK) that are more resilient to reordering, we reexamine this constraint. We show through an analytical model that increasing line rates improves the operating conditions for time-based loss detection methods, such as the one used in RACK. Further, in a set of testbed experiments representative of wide-area backbone networks, we evaluate the performance of TCP flows traversing a load-balanced switch. The results suggest that at typical conditions for backbone networks, the deployment of a load-balanced switch has a negligible impact on the performance of TCP with RACK at line rates of 10 Gbps or more. Our results suggest that switch designs that were previously thought to be unsuitable can be utilized in high-speed backbone networks, thanks to the relaxation of the in-sequence delivery constraint.
-
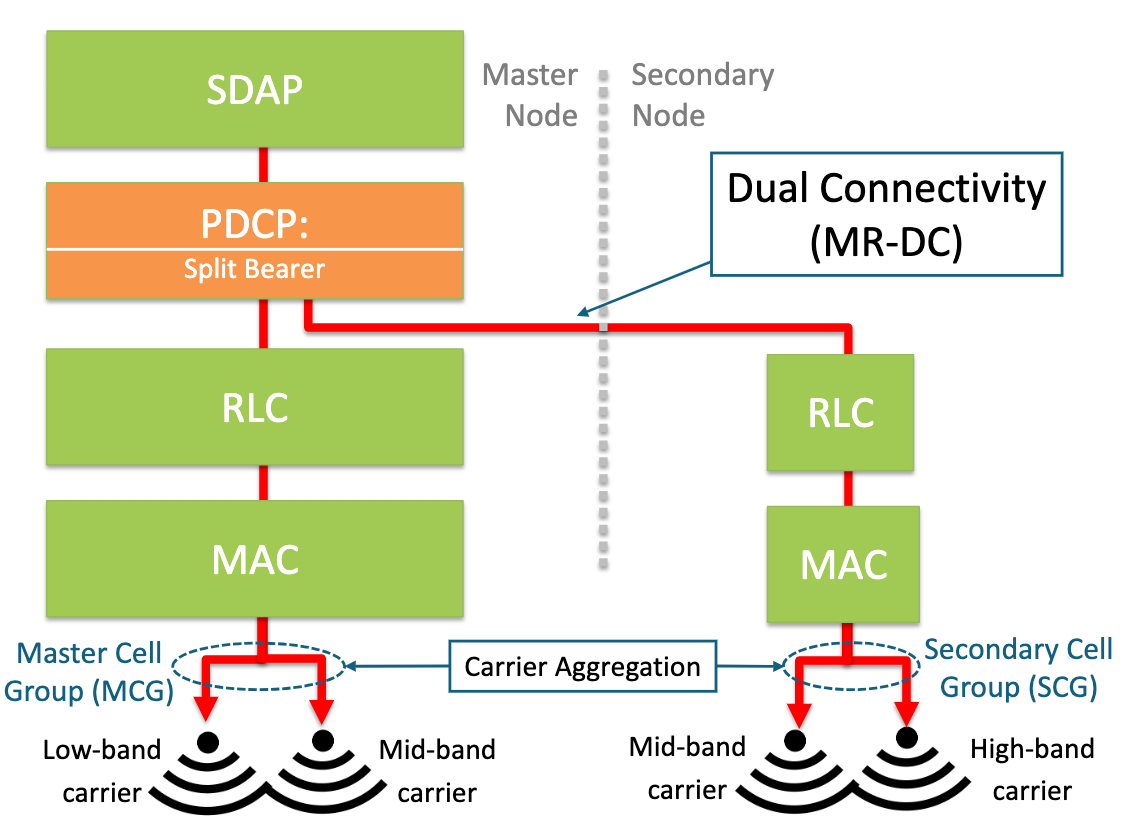 Modeling and Optimizing Dual-Connectivity Activation in Cellular NetworksIn revision, 2026
Modeling and Optimizing Dual-Connectivity Activation in Cellular NetworksIn revision, 2026Multi-Radio Dual-Connectivity (MR-DC) enables mobile network operators to use spectrum resources from multiple base stations simultaneously. In current deployments, MR-DC is activated through rule-based heuristic policies with parameters that are difficult to adjust systematically. Therefore, it is an open problem to identify the conditions under which MR-DC should be activated to achieve performance targets without compromising efficiency. In this work, we formulate the MR-DC activation problem as an analytical dual-threshold optimization framework. We develop a Multi-Regime Markov Fluid Queue (MRMFQ) model that mathematically characterizes the data backlog at and below the Packet Data Convergence Protocol (PDCP) layer under varying threshold policies, wireless link conditions, and traffic dynamics. Building on this model, we introduce an efficient numerical optimization method to determine the optimal activation and deactivation thresholds for MR-DC. As a case study, we optimize user energy efficiency subject to average delay constraints. The results demonstrate that the proposed dual-threshold policy significantly improves energy efficiency, while reducing the average delay and unnecessary MR-DC switching events. This model-based approach offers insight into MR-DC threshold design in terms of several useful key performance indicators and provides a foundation for implementations in current systems and future software-defined Radio Access Networks.
2024
-
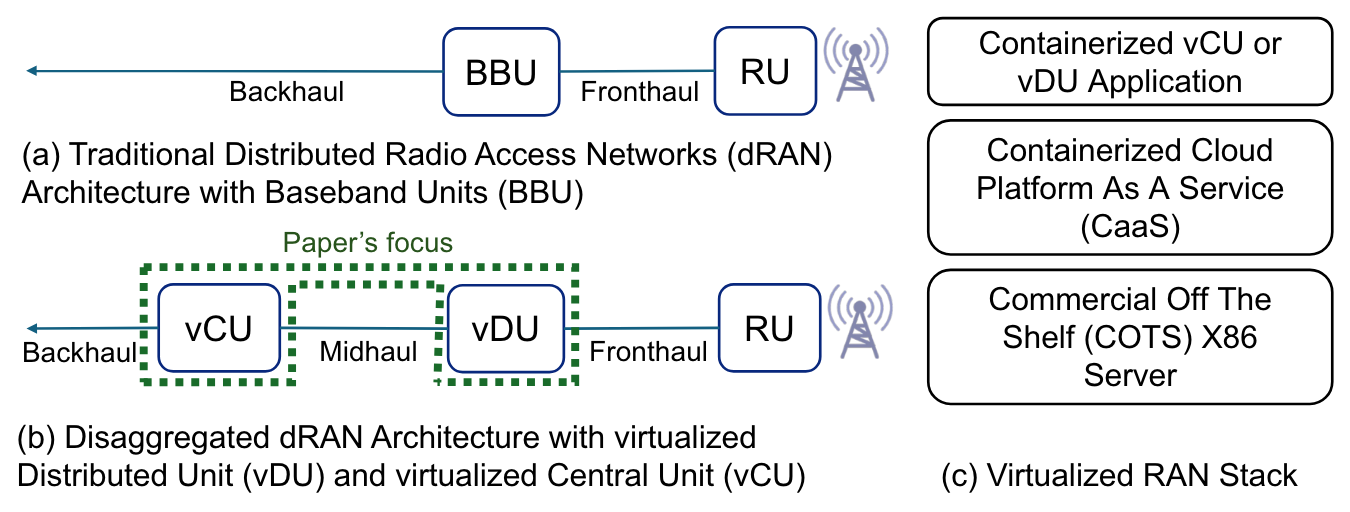 Designing Reliable Virtualized Radio Access NetworksUfuk Usubütün, André Gomes, Shankaranarayanan Puzhavakath Narayanan, Matti Hiltunen, and 1 more authorIn GLOBECOM 2024 - IEEE Global Communications Conference, 2024
Designing Reliable Virtualized Radio Access NetworksUfuk Usubütün, André Gomes, Shankaranarayanan Puzhavakath Narayanan, Matti Hiltunen, and 1 more authorIn GLOBECOM 2024 - IEEE Global Communications Conference, 2024As virtualization of Radio Access Networks (RAN) gains momentum, understanding the impact of hardware and software disaggregation on resiliency becomes critical to meet the high availability requirements of mobile networks. Our paper presents an analytical model, using continuous time Markov chains, to study the impact of virtualization and disaggregation on RAN availability. Our evaluation, assuming typical parameter value ranges for failure and recovery rates, points to containerized platforms reliability as a constraint on vRAN availability. We also find that with active-passive replication, increasing hardware replication factor beyond 2 may not bring any benefits unless failover times are reduced. We also compare the reliability of centralized and distributed virtualized central units.
2023
-
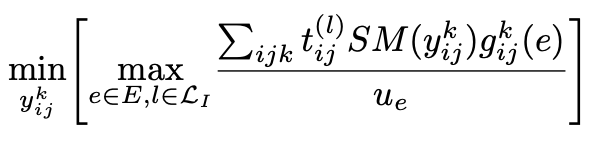 Oblivious Routing Using Learning MethodsIn GLOBECOM 2023 - IEEE Global Communications Conference, 2023
Oblivious Routing Using Learning MethodsIn GLOBECOM 2023 - IEEE Global Communications Conference, 2023Oblivious routing of network traffic uses pre-determined paths that do not change with changing traffic patterns. It has the benefit of using a fixed network configuration while robustly handling a range of varying and unpredictable traffic. Theoretical advances have shown that the benefits of oblivious routing are achievable without compromising much capacity efficiency. For oblivious routing, we only assume knowledge of the ingress/egress capacities of the edge nodes through which traffic enters or leaves the network. All traffic patterns possible subject to the ingress/egress capacity constraints (also known as the hose constraints) are permissible and are to be handled using oblivious routing. We use the widely deployed segment routing method for route control. Furthermore, for ease of deployment and to not deviate too much from conventional shortest path routing, we restrict paths to be 2-segment paths (the composition of two shortest path routed segments). We solve the 2-segment oblivious routing problem for all permissible traffic matrices (which can be infinitely-many). We develop a new adversarial and machine-learning driven approach that uses an iterative gradient descent method to solve the routing problem with worst-case performance guarantees. Additionally, the parallelism involved in descent methods allows this method to scale well with the network size making it amenable for use in practice.
-
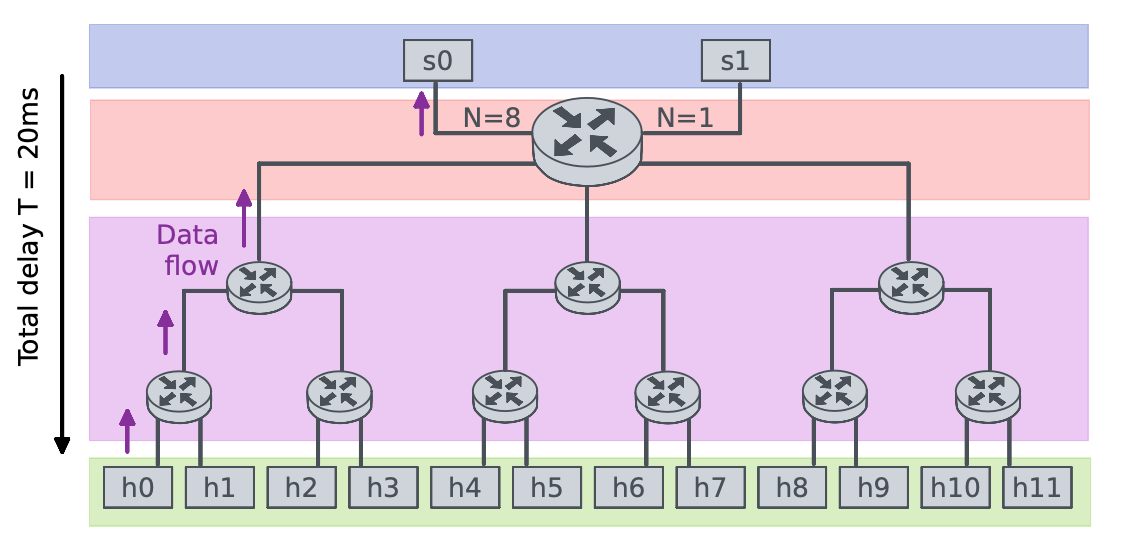 Do Switches Still Need to Deliver Packets in Sequence? - BEST PAPER AWARDUfuk Usubütün, Fraida Fund, and Shivendra PanwarIn HPSR 2023 - IEEE 24th International Conference on High Performance Switching and Routing, 2023
Do Switches Still Need to Deliver Packets in Sequence? - BEST PAPER AWARDUfuk Usubütün, Fraida Fund, and Shivendra PanwarIn HPSR 2023 - IEEE 24th International Conference on High Performance Switching and Routing, 2023Internet switches become harder and costlier to build for higher line rates and switch capacities. In-sequence delivery of packets has traditionally been a constraint on switch designs because TCP loss detection was considered vulnerable to out-of-sequence arrivals. For this reason, extremely efficient and simple designs, such as the Load Balanced Birkhoff-von Neumann Switch, were considered impractical. However, we reevaluate this constraint considering modern TCP implementations with loss detection algorithms like Recent Acknowledgment (RACK) that are more resilient to out-of-order arrivals. In a set of testbed experiments representative of wide area core networks, we evaluated the performance of TCP flows traversing a load balanced switch that reorders some packets within a flow. We show that widely deployed and standard TCP implementations of the last decade achieve similar performance when traversing a load balanced switch as they do when there is no reordering. Furthermore, we also verified that an increase in the line rate leads to favorable conditions for time based loss detection methods, such as the one used in RACK. Our results, if further validated, suggest that switch designs that were previously thought to be unsuitable can potentially be utilized, thanks to the relaxation of the in-sequence delivery constraint.